web容器是怎么解析http报文的
本篇内容主要讲解"web容器是怎么解析http报文的",感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习"web容器是怎么解析http报文的"吧!
摘要
http报文其实就是一定规则的字符串,那么解析它们,就是解析字符串,看看是否满足http协议约定的规则。
start-line: 起始行,描述请求或响应的基本信息*( header-field CRLF ): 头CRLF[message-body]: 消息body,实际传输的数据
jetty
以下代码都是jetty9.4.12版本
如何解析这么长的字符串呢,jetty是通过状态机来实现的。具体可以看下org.eclipse.jetty.http.HttpParse类
public enum State { START, METHOD, 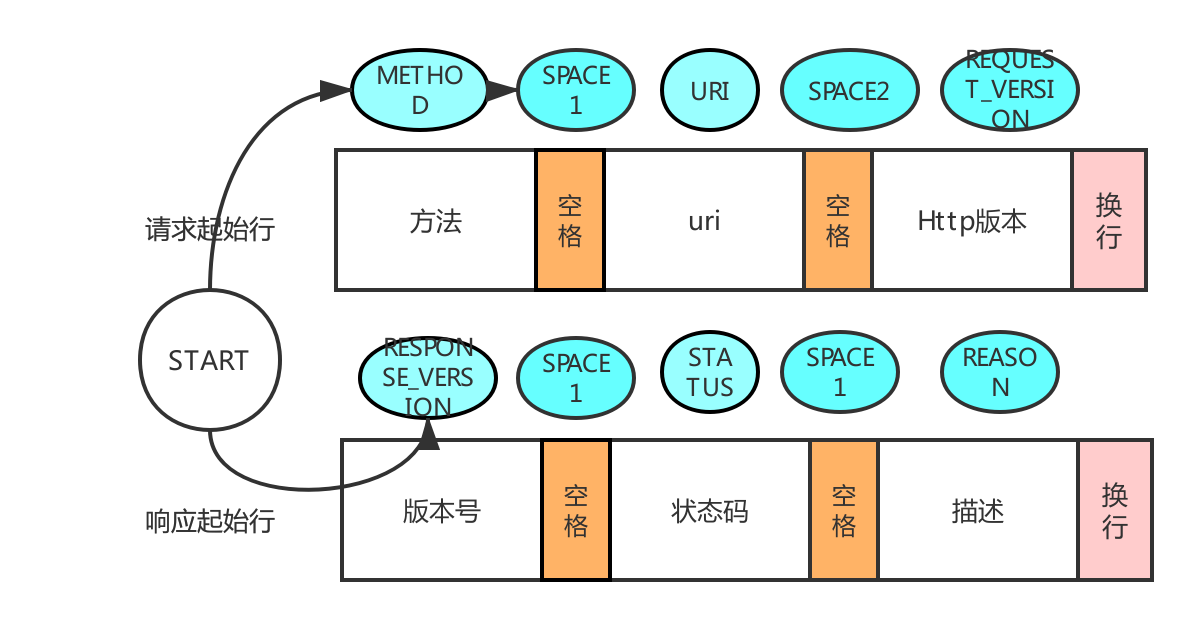, SPACE1, STATUS, URI, SPACE2, REQUEST_VERSION, REASON, PROXY, HEADER, CONTENT, EOF_CONTENT, CHUNKED_CONTENT, CHUNK_SIZE, CHUNK_PARAMS, CHUNK, TRAILER, END, CLOSE, // The associated stream/endpoint should be closed CLOSED // The associated stream/endpoint is at EOF }总共分成了21种状态,然后进行状态间的流转。在parseNext方法中分别对起始行 -> header -> body content分别解析
public boolean parseNext(ByteBuffer buffer) { try { // Start a request/response if (_state==State.START) { // 快速判断 if (quickStart(buffer)) return true; } // Request/response line 转换 if (_state.ordinal()>= State.START.ordinal() && _state.ordinal()= State.CONTENT.ordinal() && _state.ordinal()0 && _headResponse) { setState(State.END); return handleContentMessage(); } else { if (parseContent(buffer)) return true; } } return false; } 整体流程
整体有三条路径
开始 -> start-line -> header -> 结束
开始 -> start-line -> header -> content -> 结束
开始 -> start-line -> header -> chunk-content -> 结束
起始行
start-line = request-line(请求起始行)/(响应起始行)status-line
请求报文解析状态迁移
请求行:START -> METHOD -> SPACE1 -> URI -> SPACE2 -> REQUEST_VERSION响应报文解析状态迁移
响应行:START -> RESPONSE_VERSION -> SPACE1 -> STATUS -> SPACE2 -> REASON
header 头
HEADER 的状态只有一种了,在jetty的老版本中还区分了HEADER_IN_NAM, HEADER_VALUE, HEADER_IN_VALUE等,9.4中都去除了。为了提高匹配效率,jetty使用了Trie树快速匹配header头。
static { CACHE.put(new HttpField(HttpHeader.CONNECTION,HttpHeaderValue.CLOSE)); CACHE.put(new HttpField(HttpHeader.CONNECTION,HttpHeaderValue.KEEP_ALIVE)); // 以下省略了很多了通用header头content
请求体:
CONTENT -> END,这种是普通的带Content-Length头的报文,HttpParser一直运行CONTENT状态,直到最后ContentLength达到了指定的数量,则进入END状态
chunked分块传输的数据
CHUNKED_CONTENT -> CHUNK_SIZE -> CHUNK -> CHUNK_END -> END
undertow
undertow是另一种web容器,它的处理方式与jetty有什么不同呢
状态机种类不一样了,io.undertow.util.HttpString.ParseState
public static final int VERB = 0; public static final int PATH = 1; public static final int PATH_PARAMETERS = 2; public static final int QUERY_PARAMETERS = 3; public static final int VERSION = 4; public static final int AFTER_VERSION = 5; public static final int HEADER = 6; public static final int HEADER_VALUE = 7; public static final int PARSE_COMPLETE = 8;
具体处理流程在HttpRequestParser抽象类中
public void handle(ByteBuffer buffer, final ParseState currentState, final HttpServerExchange builder) throws BadRequestException { if (currentState.state == ParseState.VERB) { //fast path, we assume that it will parse fully so we avoid all the if statements // 快速处理GET final int position = buffer.position(); if (buffer.remaining() > 3 && buffer.get(position) == 'G' && buffer.get(position + 1) == 'E' && buffer.get(position + 2) == 'T' && buffer.get(position + 3) == ' ') { buffer.position(position + 4); builder.setRequestMethod(Methods.GET); currentState.state = ParseState.PATH; } else { try { handleHttpVerb(buffer, currentState, builder); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { throw new BadRequestException(e); } } // 处理path handlePath(buffer, currentState, builder); // 处理版本 if (failed) { handleHttpVersion(buffer, currentState, builder); handleAfterVersion(buffer, currentState); } // 处理header while (currentState.state != ParseState.PARSE_COMPLETE && buffer.hasRemaining()) { handleHeader(buffer, currentState, builder); if (currentState.state == ParseState.HEADER_VALUE) { handleHeaderValue(buffer, currentState, builder); } } return; } handleStateful(buffer, currentState, builder); }与jetty不同的是对content的处理,在header处理完以后,将数据放到io.undertow.server.HttpServerExchange,然后根据类型,有不同的content读取方式,比如处理固定长度的,FixedLengthStreamSourceConduit。
到此,相信大家对"web容器是怎么解析http报文的"有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!



